Bash - Reference Sheet
in CS 101
Bash is a Unix shell and command language. It has been distributed widely as the default login shell for most Linux distributions and Apple’s macOS/OS X. Bash typically runs in a text window where you can type commands, telling the computer what to do.
Bash was written for the GNU Project as a free software replacement for the Bourne shell. The name “Bash” is an acronym for Bourne-again shell, a pun on the word Bourne and “born again”.
System Information
uname -a # Display Linux system information
uname -r # Display kernel release information
uptime # Show how long the system has been running + load
hostname # Show system host name
hostname -I # Display the IP addresses of the host
last reboot # Show system reboot history
date # Show the current date and time
w # Display who is online
whoami # Who you are logged in as
Hardware Information
cat /proc/cpuinfo # Display CPU information
cat /proc/meminfo # Display memory information
free # Display free and used memory
free -h # -h for human readable
free -m # -m for MB
free -g # -g for GB
Performance Monitoring & Stats
top # Display and manage the top processes
vmstat 1 # Display virtual memory statistics
free -h # Display free and used memory ( -h for human readable, -m for MB, -g for GB.)
watch df -h # Execute "df -h", showing periodic updates
User Information & Management
id # Display the user and group ids of your current user.
last # Display the last users who have logged onto the system.
w # Show who is logged in and what they are doing.
File & Directory Commands
ls -al # List all files in a long listing (detailed) format
pwd # Display the present working directory
touch file # Create a file
mkdir directory # Create a directory
rm file # Remove (delete) file
rm -r directory # Remove the directory and its contents recursively
cp file1 file2 # Copy file1 to file2
cp -r source_directory destination # Copy source_directory recursively to destination. If destination exists, copy source_directory into destination, otherwise create destination with the contents of source_directory.
mv file1 file2 # Rename or move file1 to file2. If file2 is an existing directory, move file1 into directory file2
cat file # View the contents of file
cat > file # Replace the contents of file
head file # Display the first 10 lines of file
tail file # Display the last 10 lines of file
tail -f file # Display the last 10 lines of file and "follow" the file as it grows.
The vi Editor
vi is a text editor that was created for the Unix operating system.
vi file # Open file in the vi editor
Here are some file management commands in vi.
:w name # Write edit buffer to file name
:wq # Write to file and quit
:q! # Quit without saving changes
ZZ # Same as :wq
:sh # Execute shell commands(<ctrl> d)
:i # Turn on edit/insert mode
Process Management
ps # Display your currently running processes
ps -ef # Display all the currently running processes with more information
top # Display and manage the top processes
kill pid # Kill process with process ID of pid
File Permissions
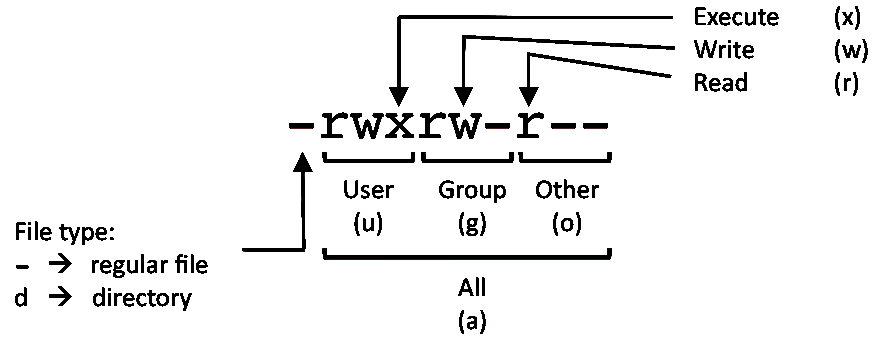
PERMISSION EXAMPLE
U G W
rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename
rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename
rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename
rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename
rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename
LEGEND
U = User
G = Group
W = World
r = Read
w = write
x = execute
- = no access
Networking
ping host # Send ICMP echo request to host
host domain # Display DNS ip address for domain
hostname -i # Display the network address of the host name.
hostname -I # Display all local ip addresses
wget http://domain.com/file # Download http://domain.com/file
Searching
grep pattern file # Search for pattern in file
grep -r pattern directory # Search recursively for pattern in directory
locate name # Find files and directories by name
find /home/john -name 'prefix*' # Find files in /home/john that start with "prefix".
find /home -size +100M # Find files larger than 100MB in /home
Disk Usage
df -h # Show free and used space on mounted filesystems
df -i # Show free and used inodes on mounted filesystems
du -ah # Display disk usage for all files and directories in human readable format
du -sh # Display total disk usage off the current directory
Directory Navigation
cd .. # To go up one level of the directory tree. (Change into the parent directory.)
cd # Go to the $HOME directory
cd /etc # Change to the /etc directory